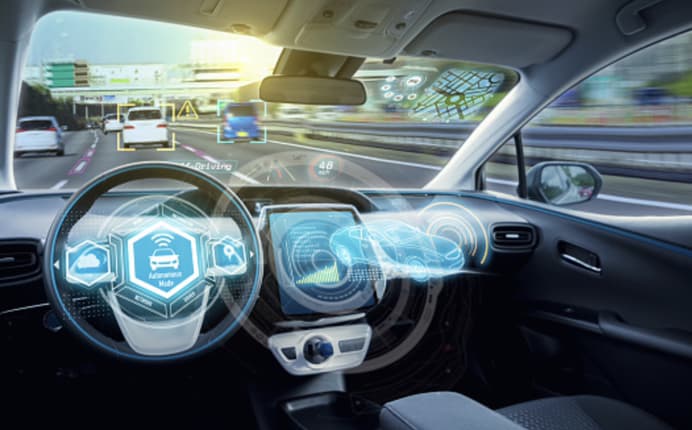
Driverless cars are equipped with a range of safety features designed to protect passengers and other road users. Here are some of the key safety features that are typically found in autonomous vehicles:
1. Sensor Technology:
Autonomous vehicles are equipped with an array of sensors, including cameras, radar, lidar, and GPS. These sensors enable the car to detect obstacles, other vehicles, and pedestrians, and to navigate the road safely.
2. Advanced Computing Systems:
computers that control driverless cars are capable of processing large amounts of data in real-time, allowing the vehicle to respond quickly to changes in the environment.
3. Redundant Systems:
Many autonomous vehicles have redundant systems, including backup sensors and computers, to ensure that the car can continue to operate safely even if one system fails.
4. Constant Monitoring:
Driverless cars are constantly monitoring their surroundings and collecting data on their performance. This data is analyzed by the vehicle’s onboard computers, which can detect and respond to potential safety issues.
5. Remote Monitoring:
Some autonomous vehicles are also monitored remotely by human operators, who can take control of the vehicle if necessary.
6. Safety Testing:
Autonomous vehicles undergo extensive safety testing to ensure that they meet high safety standards. This testing includes simulations, closed-course testing, and real-world testing.
7. Cybersecurity Measures:
Driverless cars are also equipped with cybersecurity measures to protect against hacking and other cyber threats.
Overall, driverless cars are designed with safety as a top priority. The combination of advanced sensor technology, computing systems, redundancy, monitoring, testing, and cybersecurity measures all work together to make autonomous vehicles safe for passengers and other road users.